Purpose
This process enables the Project Board to make the key decisions for the project and to remain accountable for its overall direction. The Project Board establishes overall control while delegating day‑to‑day management to the Project Manager. The Board acts as the interface with the organisation, ensuring control is exercised at every stage, that clear communication with the Project Manager is maintained, and that post‑project benefits are reviewed.
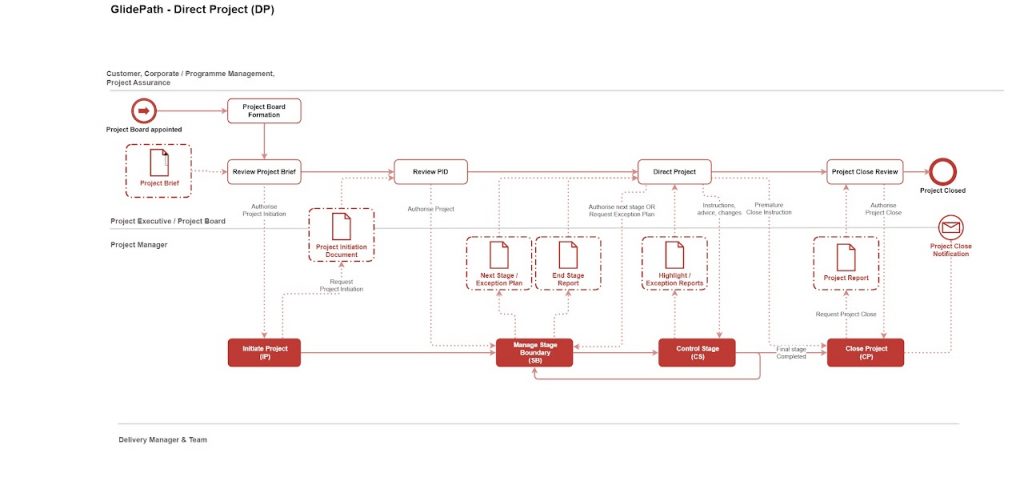
Directing a project comprises five main activities:
- Authorise the Initiation Stage to start
- Authorise delivery stages to start
- Review stage performance and authorise stage boundaries (either permitting the next stage to begin or approving an Exception Plan to complete the current stage)
- Provide ad‑hoc direction during the project
- Authorise project closure
Process flow
Process flow Directing a project begins with appointing the Project Board, which reviews and authorises project initiation. The core steps are:
- Initiate the project – define the work required to deliver the agreed products. The Project Manager prepares the Project Initiation Document (PID), which the Project Board reviews and authorises.
- Manage the Stage Boundary -monitor the current stage, plan the next stage and update the Project Plan. The Project Manager submits End Stage Reports and any Exception Plans to the Project Board for review and decision.
- Control the Stage – the Project Manager runs day‑to‑day management of the stage, applying the controls established at initiation. Highlight Reports and Exception Reports are submitted as required to keep the Project Board informed of progress and issues.
- Close the Project – when objectives have been met and products accepted, the Project Manager submits the Project Report and a request to close the project. The Project Board confirms acceptance and closes the project.
Directing a project phase starts with the appointment of the Project Board, which reviews and authorizes the project initiation. The steps involved are:
- Initiate a project by defining the work that needs to be done to deliver the required artefacts. Project Initiation Documentation (PID) is created by the Project Manager and reviewed by the Project Board.
- Manage the Stage Boundary by monitoring the current stage, planning the next stage plan and updating the project plan. Exception Plan and End Stage Report are submitted to the Project Board for review.
- Control Stage involves day-to-day management of a stage of the project by the Project Manager. The controls that were set up initially are exercised under this stage. Highlight and Exception reports are to submitted to mark the completion of this process.
- Close Project process is the check point where the project has reached its objectives and the products have been accepted. Project report is submitted along with the request to close the project.
Inputs
- Authorisation to initiate the project from the Project Board
- Project Brief (from Start Up)
- Initiation Stage Plan (from Start Up)
Key Deliverables
Project Initiation Document; project approach, business case, benefits, project controls, team structure and role descriptions.
Exception Plan; cause of exception, consequences of deviation, options, recommendation, lessons and major risks.
End Stage Reports; review of the business case, project objectives, stage objectives, team performance products, risks and forecasts.
Highlight Reports; status summary, reporting periods, change request and lesson log.
Project Plan; prerequisites, approach, assumptions, budget and schedule.
